Financial Statements 1
These are prepared at the end of a given trading period to determine the profit and losses of the business, and also to show the financial position of the business at a given time.
They includes; trading account, profit and loss account, trading profit and loss account and the balance sheet.
They are also referred to as the final statements.
The trading period is the duration through which the trading activities are carried out in the business before it decides to determines it performances in terms of profit or loss.
It may be one week, month, six months or even a year depending on what the owner wants.
Most of the business use one year as their trading period.
It is also referred to as the accounting period
At the end of the accounting period, the following takes place;
• All the accounts are balanced off
• A trial balance is extracted
• Profit or loss is determined
• The balance sheet is prepared
Determining the profit or loss of a business
When a business sells its stock above the buying price/cost of acquiring the stock, it makes a profit, while if it sells below it makes a loss.
The profit realized when the business sell it stock beyond the cost is what is referred to
as the gross profit, while if it is a loss then it is referred to as a gross loss.
It is referred to as the gross profit /loss because it has not been used to cater
for the expenses that may have been incurred in selling that stock, such as the salary of the salesman, rent for the premises, water bills, etc.
It therefore implies that the businessman cannot take the whole gross profit for its
personal use but must first deduct the total cost of all other expenses that may have been incurred.
The profit realized after the cost of all the expenses incurred has been deducted is what becomes the real profit for the owner of the business, and is referred to as Net profit.
The net profit can be determined through calculation or preparation of profit and loss account.
In calculating the gross profit, the following adjustments are put in place
Return inwards/Sales return:
These are goods that had been sold to the customers, but they have returned them to the business for one reason or the other.
It therefore reduces the value of sales, and is therefore subtracted from sales to obtain the net sales
Therefore Net sales = Sales – Return inwards
Return outwards/purchases return: - these are goods that had been bought from the suppliers to the business and have been returned to them for one reason
It reduces the purchases and is therefore subtracted from the purchases to obtain the net purchases.
Drawings:
This refers to goods that the owner of the business has taken from the business for his own use.
It reduces the value of purchases, and is therefore subtracted from purchases when determining the net purchases.
It is different from the other drawing in that it is purely goods and not money.
Carriage inwards/Carriage on purchases: - this is the cost incurred by the suppliers in transporting the goods from his premises to the customers business.
It is treated as part of the purchases, and therefore increases the value of purchases.
It is added to purchases to determine the actual value of purchases/Net purchases.
Therefore Net Purchases = Purchases + Carriage inwards – Return Outwards - Drawings.
Carriage outwards/Carriage on sales:
- This is the cost that the business has incurred in transporting goods from its premises to the customer’s premises.
The cost reduces the business profit that would have been realized as a result of the sale, and is therefore treated as an expense and is
subtracted from the gross profit, before determining the net profit.
Opening stock is the stock of goods at the beginning of the trading period, while the closing stock is the stock of the goods at the end of the trading period.
Gross profit is therefore calculated as follows;
Gross Profit = Sales – Return inwards – (Opening stock + Purchases + carriage inwards – Return outwards – Closing stock)
Or
Gross profit = Net sales – Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) COGS = Opening Stock + Net Purchases – Closing stock
Net Profit = Gross profit – Total expenses.
Trading Account
This is prepared by the business to determine the gross profit/loss during that trading period
It takes the following format:
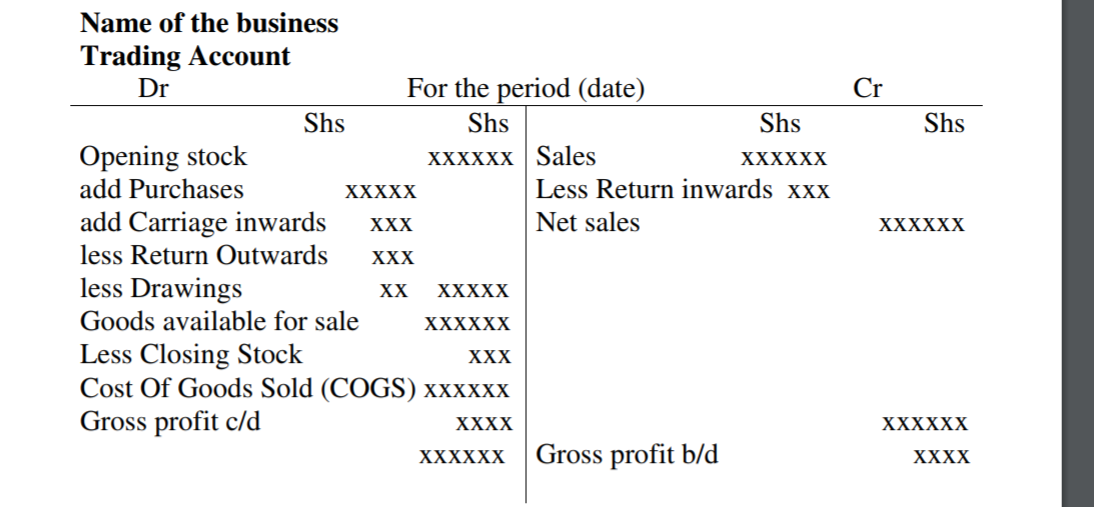
The trading account is completed by the time the gross profit b/d is determined
For example
The following balances were obtained from the books of Ramera Traders for the year ending may 31st 2010.
Sales 670 000
Purchases 380 000
Return inwards 40 000
Carriage outwards 18 000
Return outwards 20 000
Carriage inwards 10 000
Additional information:
Required;
Prepare Ramera Traders trading account for the period ending 31st May 2010
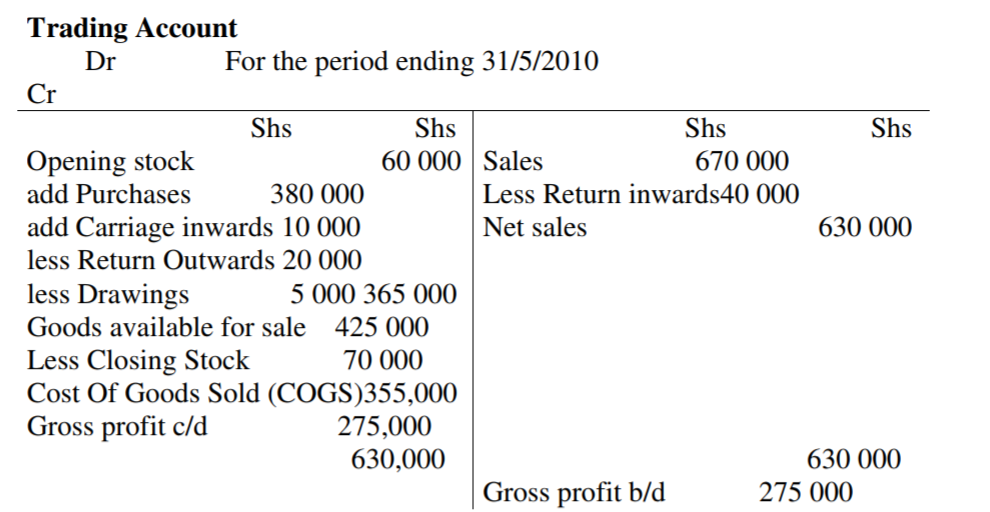
NB: Carriage outwards is not an item of Trading account, but profit and loss
account as an expense.
Financial Statements 1 | Financial Statements 2 |
Financial Statements 3 | Financial Statements 4 |
Scholarship 2025/26
Current Scholarships 2025/2026 - Fully Funded
Full Undergraduate Scholarships 2025 - 2026
Fully Funded Masters Scholarships 2025 - 26
PhD Scholarships for International Students - Fully Funded!
Funding Opportunities for Journalists 2025/2026
Funding for Entrepreneurs 2025/2026
***
