Combination Keys on Keyboard and their Functions
Combination Keys on Keyboard and their Functions; ☆☛✅ A full list of Combination Keys & definition.
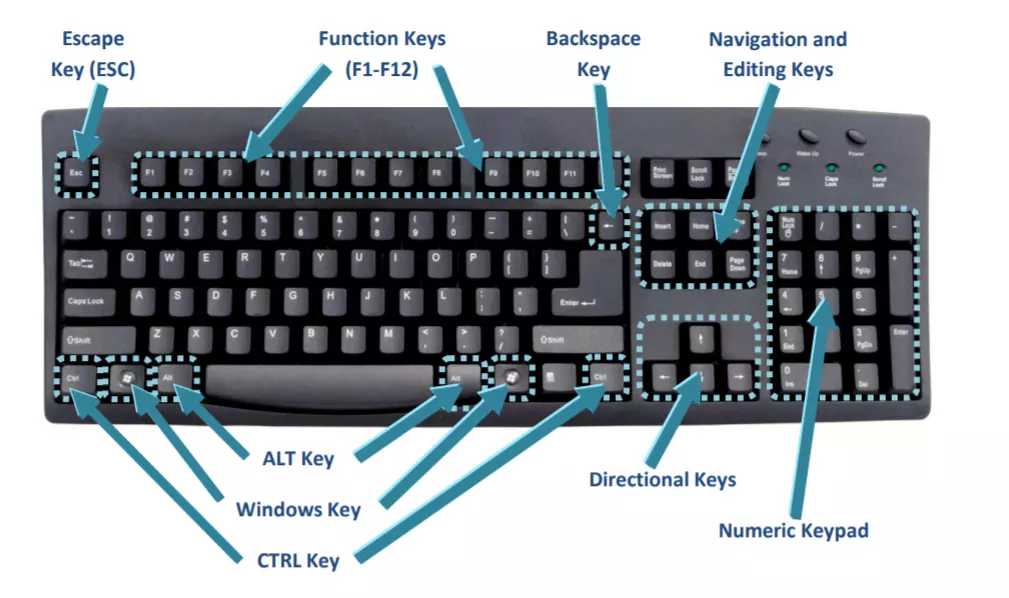
A key combination is the use of two or more keys on a keyboard to generate a specific result. These keys are pressed either at the same time, or one after the other while holding down each key until the last key is pressed.
Alternate (ALT) + Right Arrow will go forward to a page you've previously accessed in your current browser session
ALT + Left Arrow will go back to a page you've previously accessed in your current browser session (Remember that the Backspace key will also go back to a page you've previously accessed in your current browser session)
Control (CTRL) + F will open a Find dialog to search a page for text.
CTRL+ESC = Open Start menu
CTRL+A = Highlight items in window
CTRL+Z = Undo
Holding down CTRL + ALT and pressing the letter C will insert the copyright symbol (©), unless you have already assigned the letter C to a quick launch shortcut, in which case it will launch the associated application.
Press the Windows key + the Pause/Break key to open up the System Properties dialog.
SHIFT+F10: Equivalent of right-click
SHIFT+DEL: Deletes immediately without removing to the Recycle Bin
Press Shift when inserting a CD-ROM and you can skip auto-run
Pressing Shift while holding down CTRL and dragging to the desktop or to a folder creates an instant shortcut.
Additional shortcuts for use with the Windows key (the one with the Windows logo on it):
Windows ⊞: Display Start menu.
Windows ⊞ + D: Minimize or restore all Windows (Win98 and later only).
Windows ⊞ + Tab: Cycle through buttons on taskbar; when you release the Windows key, just press the space bar or ENTER key to switch to the window which corresponds to the currently highlighted button.
Windows ⊞ + Ctrl + F: Display find: computer.
Windows ⊞ + F1: Display Help.
Windows ⊞ + break: Display system properties dialog box.
You can start any program you choose with three combination keys (CTRL + ALT + "CHARACTER", where "character" represents a character you designate) simply by placing its icon on the desktop, right-clicking on it, and choosing Properties.
When the properties dialog displays, select the Shortcut tab, then click your mouse pointer in the Shortcut keys text box and type in whatever character (a letter, number, etc.) you want in the box.
The keywords "CTRL + ALT +" will appear automatically in front of the character you typed.
Click OK to close the dialog, and press CTRL + ALT + "CHARACTER" to test it.
The program should start immediately. This combination key/shortcut option can save you a few seconds from having to find it on the Start menu or minimize all windows in order to double-click its icon with your mouse on the desktop.
Your only challenge now will be remembering which shortcut character you designated for each program.
We recommend using the first letter of the program.
When you have more than one program beginning with the same letter, use either the next letter in its name or a number.
Windows key ⊞ + M will minimize all currently running programs on your desktop.
In any Windows program, when you see a word with an underlined letter, such as Ok or Print, you can hold down the Alternate (ALT) key and depress the underlined letter to perform that action without having to click on it with your mouse pointer.
On a drop-down menu, however, you don't need to use the ALT key; just depress the underlined letter to execute the function.
Read your software's Help files and/or examine your software's menus for additional shortcuts.
For instance, the F1 function key usually starts the program's Help engine without having to choose it from the menu.
Holding down the Windows Start key (⊞; it's usually located next to the ALT or Control (CTRL) key), and depressing the E key will start Windows Explorer without having to choose it from the Start | Programs menu.
Holding down the CTRL key while depressing either the left or right arrow keys will cause your cursor to jump from one whole word to another in any word processor.
CTRL + C will copy any highlighted text to your Windows Clipboard.
CTRL + V will paste any text from your Windows Clipboard to the point where your cursor is currently located.
Pressing the Home key will move the cursor or screen display to the very beginning of a line in a Windows document.
CTRL + End will move your cursor or screen display to the very end of a Windows document or browser page view (in MSIE 5.5 and Netscape 6 only).
Holding down the CTRL + Shift keys while depressing either of your arrow keys
will highlight text and/or select graphics in the direction of the arrow key you choose.
CTRL + Shift + Home will select all text and/or graphics from the present cursor position to the very beginning of a Windows document.
CTRL + Shift + End will select all text and/or graphics from the present cursor position to the very end of a Windows document.
In Windows Explorer, holding down the CTRL key while clicking your mouse pointer on file names individually will allow you to select multiple files for copying from one location to another.
In Windows Explorer, if you want to select all files within a certain sequence, first highlight the initial file in the sequence, then scroll down to the last file in the sequence, hold down the CTRL + Shift keys and click your mouse pointer on the last file to highlight all files between those two files.
You can also skip files and continue selecting or even go back and unselect files by holding down the CTRL key and clicking your mouse pointer on the additional files or the previous files you decided against selecting.
When a command button has the focus (is outlined or highlighted) during a program's execution, pressing either the Enter key or the Space Bar will execute that command button's function.
When viewing either software or Web pages with data fields or separate textboxes, use the Tab key to jump from one field or box to the next. Hold down the Shift key and depress the Tab key to reverse the direction you jump from one field or box to the next.
ALT + F4 will close whichever program you are currently using. To close additional programs using this shortcut, click on the program's button on the Windows taskbar then hold down the ALT key and depress the F4 key.
The Windows Menu key (⊞; it's usually located below the right shift key) activates a pop-up menu identical to the one activated by your right mouse button. It's a quick way to Undo an action, Cut, Copy, Paste, Delete or Select All on-screen.
Holding down the Windows Start key ⊞ and depressing the F key will open the File Search dialog without having to go through two menu levels on the Start | Programs menu. Pressing the F3 key from your Windows desktop will do the same thing.
Holding down the ALT key and depressing the TAB key will display on-screen currently running programs to which you can switch your screen view. An icon is highlighted when a box encases it. Continue holding the ALT key and press the TAB key repeatedly to cycle through the on-screen icons. When you highlight the icon of the program to which you want to switch, let go of the ALT key, and your PC will switch to that program on-screen. You may also reverse TAB directions by holding down the SHIFT key with the ALT key and pressing the TAB key.
To restart the Windows operating system without completely rebooting your computer, follow these steps: 1. On the Start Menu, click Shutdown. 2. Check Restart. 3. As you click Yes/OK, hold down the Shift Key. 4. Continue pressing Shift until you see the words, "Windows is now restarting." This tip does not work with Windows Me, however.
To shut down Windows without having to use the Start menu, click your mouse on your Windows taskbar or anywhere on your desktop (except on an icon), hold down the ALT key and press the F4 key. When the shut down confirmation dialog appears, make sure the option you desire is checked, and press ENTER.
Here are some keyboard shortcuts from the old days of MS DOS, but they work with Windows as well.
1. SHIFT + DELETE = Cut highlighted text onto Clipboard
2. CTRL+ INSERT = Copy highlighted text onto Clipboard
3. SHIFT + INSERT = Paste contents of Clipboard
4. SHIFT + TAB = Undo tab
5. CTRL + Q + F = Find/Replace text (used to be Find text)
6. CTRL + Q + A = Select all (used to be Find/Replace text)
7. F3 = Repeat last search
The following keyboard function keys perform the same tasks within both Windows Explorer (WinEx) and Internet Explorer (IE), with only a few differences:
F1 = Starts Help in both
F2 = Renames a file/folder in WinEx; Unassigned in IE
F3 = Activates the Find: All Files feature in both
F4 = Selects a different file/folder in both
F5 = Refreshes the current view in both
F6 = Tabs from pane to pane in WinEx; Highlights the address box in IE
F7 = Unassigned in both
F8 = Unassigned in both
F9 = Unassigned in both
F10 = Highlights the menu bar in both
F11 = Unassigned in WinEx; Sets the screen to Full Screen view in IE
F12 = Unassigned in both
More Computer Shortcut Keys and Their Functions - Click Here!